Aklan posts highest basic literacy rate in Western Visayas
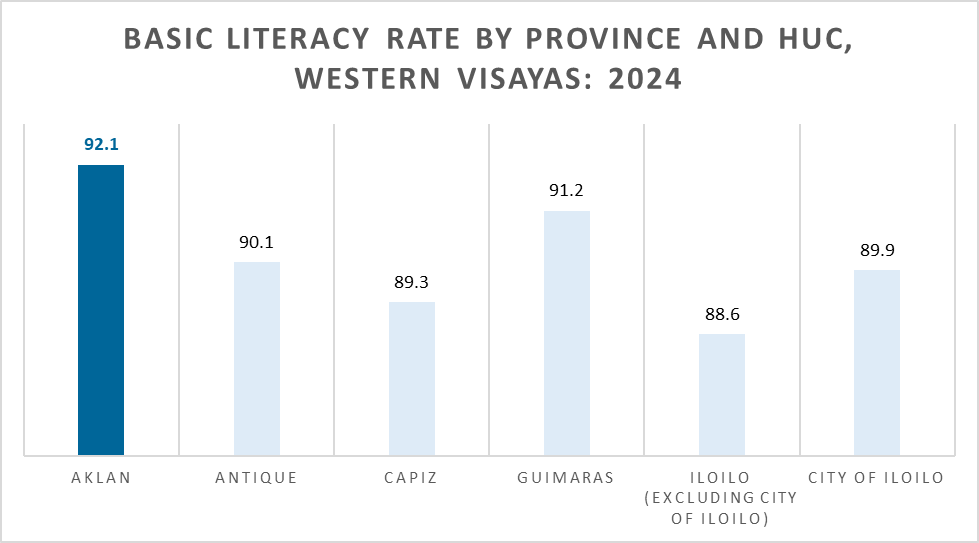
Aklan recorded the highest basic literacy rate among all provinces and highly urbanized cities in Western Visayas, reaching 92.1% among individuals aged 5 years and older, according to the 2024 Functional Literacy, Education, and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS). This means that roughly 9 in every 10 Aklanons—or about 522,000 people—can read and write a simple message in any language or dialect with understanding, and perform basic mathematical operations.
Following Aklan were Guimaras with 91.2 percent and Antique with 90.1 percent. Meanwhile, Iloilo Province (excluding Iloilo City) recorded the lowest basic literacy rate in the region at 88.6 percent, followed by Capiz at 89.3 percent.
Conversely, around 28,000 individuals (5 percent) in this age group were found to be illiterate, while approximately 16,000 (2.9 percent) had low literacy, meaning they could only read and write without comprehension or numerical skills. Aklan also posted the lowest illiteracy and low literacy rates in the region.
Aklan garners highest functional literacy rate in the region
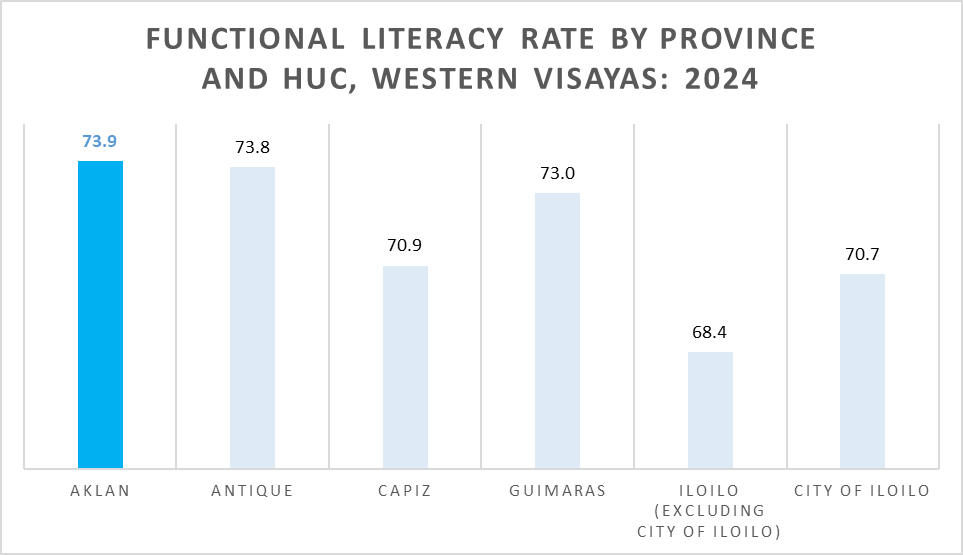
Among individuals aged 10 to 64 years old, Aklan posted the highest functional literacy rate in Western Visayas at 73.9 percent, equivalent to about 340,000 people who can read, write, compute, and comprehend. This was the highest rate recorded among all provinces and highly urbanized cities in the region.
Antique followed closely with 73.8 percent, while Guimaras came next at 73.0 percent. On the other hand, Iloilo Province (excluding Iloilo City) registered the lowest functional literacy rate in the region at 68.6 percent, followed by Iloilo City at 70.7 percent and Capiz at 70.9 percent.
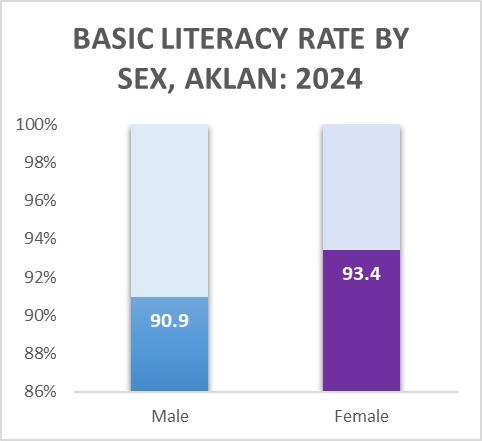
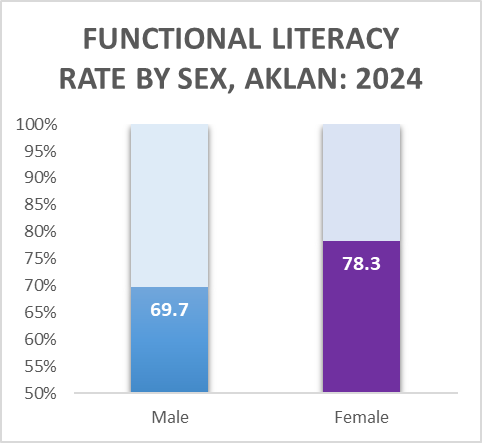
Higher basic and functional literacy among females than males
Among individuals aged 5 years and over, females recorded a higher basic literacy rate at 93.4 percent, compared to 90.9 percent for males. Conversely, males posted higher rates of illiteracy and low literacy at 6.0 percent and 3.1 percent, respectively, while females had lower corresponding rates of 4.0 percent for illiteracy and 2.6 percent for low literacy.
Moreover, among individuals aged 10 to 64 years old, females also exhibited higher functional literacy rate at 78.3 percent compared to 69.7 percent among males.
Table 1. Number and Rate of Basically Literate Population 5 Years Old and Over by Sex, Region, Province, and Highly Urbanized Cities (HUCs), Western Visayas: 2024 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region / Province / HUCs | Population 5 Years Old and Over | Number of Basically Literate Population | Basic Literacy Rate | ||||||
Both Sexes | Male | Female | Both Sexes | Male | Female | Both Sexes | Male | Female | |
Region VI (Western Visayas) | 4,463 | 2,255 | 2,208 | 3,998ʳ | 1,992 | 2,005 | 89.6 | 88.4ʳ | 90.8 |
Aklan | 566 | 287 | 280 | 522 | 261 | 261 | 92.1 | 90.9 | 93.4 |
Antique | 563 | 287 | 276 | 508 | 257 | 251 | 90.1 | 89.3 | 91.0 |
Capiz | 769 | 388 | 381 | 686 | 337 | 349 | 89.3 | 87.0 | 91.5 |
Guimaras | 175 | 90 | 85 | 159 | 80 | 79 | 91.2 | 89.5 | 93.0 |
Iloilo (Excluding City of Iloilo) | 1,958 | 991 | 967 | 1,735 | 866 | 868 | 88.6 | 87.4 | 89.8 |
City of Iloilo | 431 | 212 | 220 | 388 | 191 | 197 | 89.9 | 90.3 | 89.6 |
Table 2. Functional Literacy for Population 10 to 64 Years Old by Sex, Region, Province, and Highly Urbanized Cities (HUCs), Philippines: 2024 | ||||||
Region / Province / HUCs | Functionally Literate | |||||
Both Sexes | Male | Female | ||||
Number | Rate (%) | Number | Rate (%) | Number | Rate (%) | |
Region VI (Western Visayas) | 2,558ʳ | 70.6 | 1,238ʳ | 66.6 | 1,320 | 74.8 |
Aklan | 340 | 73.9 | 165 | 69.7 | 175 | 78.3 |
Antique | 332 | 73.8 | 162 | 69.4 | 170 | 78.4 |
Capiz | 445 | 70.9 | 212 | 66.0 | 233 | 76.0 |
Guimaras | 104 | 73.0 | 49 | 65.7 | 56 | 80.9 |
Iloilo (Excluding City of Iloilo) | 1,080 | 68.4 | 528 | 64.9 | 552 | 72.1 |
City of Iloilo | 256 | 70.7 | 123 | 68.0 | 134 | 73.3 |
EXPLANATORY TEXT
The Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) releases its second report on the results of the 2024 Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS). This report presents the basic and functional literacy estimates at the provincial and highly urbanized city (HUC) levels. This is the first time that literacy data at these geographic levels have been generated from the FLEMMS since it was first conducted in 1989.
The 2024 FLEMMS adopted a revised operational definition and methodology for measuring basic and functional literacy as approved by the PSA Board through Resolution No. 13, Series of 2024.
Basic literacy is defined as the ability of a person to read and write a simple message in any language or dialect with understanding, and to compute or perform basic mathematical operations.
Functional literacy is the ability of a person to read, write, compute and comprehend. In addition to the basic literacy skills, functional literacy includes higher level of comprehension skills, such as integrating two or more pieces of information and making inferences based on the given information.
Basic literacy rate is computed for individuals 5 years old and over, while functional literacy rate is computed for individuals 10 to 64 years old.
ENGR. ANTONET B. CATUBUAN
Chief Statistical Specialist

